失忆性贝类毒素(Amnesic shellfish poisoning,ASP)是由多列拟菱形藻(Pseudo-nitzschia seudonitzsehia)分泌产生的毒素,其引起中毒的成分是软骨藻酸(Domoic acid,DA)[1]。部分浮游植物产生的有毒次生代谢物“藻毒素”,也可以沿食物链传递并在贝类体内积累,称为“贝毒”。人类食用含有大量贝毒的水产品后会引起中毒,甚至死亡[2]。1987年底,加拿大暴发了一种急性疾病,其特征是食用养殖贻贝的人出现胃肠道症状和神经系统异常,事后研究表明引起中毒的活性成分为DA,是一种强有力的兴奋性神经递质[3]。DA的存在可能引起中枢神经系统海马区和丘脑区与记忆有关区域的损伤,从而导致记忆的丧失。经研究发现,摄入15~20 mg DA的人群未受其影响;摄入量为60~110 mg时会引起中度胃肠道症状;摄入量为295 mg时表现出各种严重症状,可见DA的毒性具有剂量效应[4]。对贝体内DA的食用安全性进行研究,发现人类通过膳食可耐受的最大限量为20 mg/kg,因此美国FDA将DA列为严重危害人类健康的四种主要海洋生物毒素之一,加拿大首先制定了DA的安全限量标准为20 μg/g贝肉[5],欧盟和美国安全标准为20 mg/kg贝肉组织[6]。
福建是贝类养殖大省,贝类质量安全和百姓健康与海洋经济的发展息息相关。近年来,由于沿海特殊的海湾环境、气候条件,以及人类开发活动的加剧,导致福建近岸海域环境不断恶化,赤潮灾害频发,而赤潮毒素通过食物链传递富集至贝类体内,进而危害人类健康。加之养殖贝类品种繁多,生物特性各异,导致贝毒风险隐患复杂难控,食用贝类造成的中毒事件时有发生。在这种形势下,对贝类毒素的分析研究越来越重要。迄今为止,我国国家和行业共颁布的有关检测失忆性贝类毒素的标准有GB/T 5009.198—2003《贝类 记忆丧失性贝类毒素软骨藻酸的测定》、SN/T 1070—2002 《进出口贝类中记忆丧失性贝类毒素检验方法》、SN/T 1867—2007 《进出口贝类中软骨藻酸的检测方法 液相色谱-串联质谱法》和SN/T 2663—2010《贝类中失忆性贝类毒素检验方法 酶联免疫吸附法》。这四个标准已被2016年颁布的GB 5009.198—2016《食品安全国家标准 贝类中失忆性贝类毒素的测定》[7]所替代。
检测DA的主要方法有小鼠生物法(MBA)、酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)、毛细管电泳法、高效液相色谱法(HPLC)、液相色谱-质谱法(LC-MS)等[8⇓⇓⇓-12]。Quilliam M A等证明了电喷雾电离-质谱(ESI-MS)技术在检测贝类中DA和其他水产品毒素方面的潜力[13],除此之外目前已经提出了各种反相/电喷雾电离-质谱(RPLC/ESI-MS)技术检测DA[14-15]。Ciminiello P等提出了一种基于亲水作用液相色谱-质谱(HILIC/MS)检测贝类中DA 的新方法,此方法采用多反应监测采集模式(MRM),在阳性和阴性实验中DA的最低检测水平分别为63和190 ng/g[16]。Blay P等使用台式Orbitrap系统进行液相色谱-质谱(LC-MS)筛选贝类中常见的多种生物毒素,利用亲水作用色谱(HILIC)可在4 min内分离DA等毒素,检出限为3.4~14 μg/L[17]。国内有学者用液相色谱串联电喷雾离子阱质谱法测定贝类中DA[18],通过QuEChERS技术结合液相色谱-高分辨质谱测定贝类中DA[19],将免疫亲和柱净化技术结合高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱检测双壳类水产中DA[20]。由于受仪器设备的限制,国家还未颁布使用高效液相色谱-串联质谱法(High performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,HPLC-MS/MS)检测贝类中失忆性贝类毒素的标准。因此,本研究拟应用HPLC-MS/MS技术,参照GB 5009.198—2016《食品安全国家标准 贝类中失忆性贝类毒素的测定》要求,建立贝类体内DA残留的检测方法,为提高我国贝类体内DA的检测技术水平和促进水产品质量安全管理提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
LCMS-8050高效液相色谱-质谱联用仪,日本岛津公司;3-30Ks高速冷冻离心机,德国Sigma公司;电子天平,赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;Milli-Q Integral 5 超纯水一体化智能系统,美国Millipore公司;超声波清洗器,德国Wiggens公司;涡旋振荡器,德国IKA公司。
软骨藻酸标准品(DA,332±11 μmol/L)、SAX 固相萃取柱(200 mg,6 mL)、甲酸:分析纯,上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司;MAX固相萃取柱(60 mg,3 mL),美国Waters公司;甲醇、乙腈:色谱纯,MERCK公司。
1.2 样品处理
1.2.1 样品制备
用清水将贝类样品外表彻底洗净,切断闭壳肌,开壳,用水淋洗内部去除泥沙及其他外来物。将闭壳肌和连接在胶合部的组织分开,取出贝肉,沥水5 min,检出碎壳等杂物,将贝肉均质,备用。
1.2.2 样品提取
称取5 g(精确到0.01 g)试样于50 mL离心管中,加入50%甲醇溶液12 mL,涡旋混匀1 min,超声提取10 min,以10 000 r/min离心5 min,移出上清液。残渣再用5 mL 50%甲醇溶液重复提取两次,合并上清液,以50%甲醇溶液定容至25 mL,混匀。再以10 000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,待净化。
1.2.3 样品净化
准确吸取提取液5 mL于预先活化好的SAX小柱中,控制流出液速度约为每秒1滴,然后用5 mL 10%乙腈溶液淋洗,弃去流出液,用4 mL 0.3%甲酸水溶液洗脱,收集洗脱液,用0.3%甲酸水溶液稀释至4 mL(相当于1 g试样),混匀后经0.22 μm针筒过滤器过滤,滤液供高效液相色谱-串联质谱测定。
1.2.4 空白基质液
选取空白试样,按照“1.2.1~1.2.3”步骤,得到空白基质液。
1.3 质谱条件
离子源为电喷雾离子源;扫描方式为正离子扫描;雾化气流量3 L/min;加热气流量10 L/min;接口温度300℃;脱溶剂温度526℃;DL温度250℃;加热块温度400℃;干燥气流量10 L/min。
1.4 液相色谱条件
ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18超高压液相色谱柱(2.1×50 mm,1.7 μm);流速0.3 mL/min;柱温30℃;进样量1 μL。在相同梯度洗脱条件下,分别考察流动相A为甲醇溶液、流动相B为2 mmol/L乙酸铵缓冲溶液(含0.1%甲酸)和流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液、流动相B为0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液对DA响应信号的影响,梯度洗脱见表1。
表1 流动相梯度洗脱条件
Tab.1
| 时间/min Time | 流速/(mL/min) Velocity | 流动相A/% Flow phase | 流动相B/% Flow phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 10 |
| 1.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 10 |
| 3.0 | 0.3 | 10 | 90 |
| 5.0 | 0.3 | 10 | 90 |
| 5.1 | 0.3 | 90 | 10 |
| 9.0 | Stop | - | - |
1.5 净化条件及洗脱液选择
分别考察MAX(60 mg,3 mL)和SAX(200 mg,6 mL)两种固相萃取柱的净化效果,以及分别考察0.3%甲酸溶液、1.0%甲酸溶液和5.0%甲酸甲醇溶液从固相萃取柱洗脱DA的效果。将MAX固相萃取柱依次用3 mL甲醇和3 mL水活化,SAX固相萃取柱依次用6 mL甲醇、3 mL水和3 mL50%甲醇溶液活化。在一定体积的 100 μg/L DA标准溶液中加入4倍体积的50%甲醇溶液涡旋混合,准确吸取5 mL混合液,加入预先活化好的MAX和SAX固相萃取柱中,控制流出液速度约为每秒1滴,然后用5 mL 10%乙腈溶液淋洗,弃去流出液,用4 mL不同洗脱液洗脱,收集洗脱液,经0.22 μm针筒过滤器过滤,滤液供HPLC-MS/MS测定。
1.6 基质效应、线性范围和检出限
采用HPLC-MS/MS分析测定时,生物样品中的内源性物质或外源性物质会影响分析物的离子化或去溶剂化过程,使分析物的质谱响应增加或降低,从而产生基质效应[21]。本研究采用计算公式如下:
当基质效应在-20%~20%之间为弱基质效应;在-50%~-20%和20%~50%为中等基质效应;超过-50%或50%为强基质效应[22]。
用空白基质液稀释DA并定容,配制成质量浓度分别为0.5、1.0、2.0、5.0、10.0、25.0 μg/L的基质-DA标准系列工作液,利用线性回归分析计算DA线性范围。
方法的检出限(LOD)和定量限(LOQ)通常分别按3倍信噪比(S/N)和10倍信噪比所对应的样品浓度来确定[23]。
1.7 准确度和精密度
取DA标准溶液加入到5 g空白样品中,使添加水平相当于5.0、12.5、50.0 μg/kg,按“1.2.2~1.2.3”步骤进行样品处理,每个水平平行测定6次,连续测定6 d,计算回收率及日内、日间相对标准偏差(RSD)。
1.8 方法应用
利用本文建立的HPLC-MS/MS法对福州、宁德和莆田3个福建省沿海重点养殖区的136个贝类(包括牡蛎、缢蛏、贻贝、花蛤、鲍、扇贝6种贝类)样品进行DA检测分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 质谱条件优化
软骨藻酸分子式为C15H21NO6,含有氨基和多个羧基,离子化过程容易形成正离子,因此选用ESI+离子源进行分析。用DA的标准溶液通过流动注射分析(FIA)在正离子模式下进行母离子扫描,在已知化合物分子量的基础上,将扫描范围设定在200~500 m/z 之间,选择正离子模式下强度最高的[M+H]+作为母离子。通过产物离子优化,对母离子进行碰撞电离,针对自动搜索的产物离子m/z,在-0.5~+0.5 U的范围内,选择峰强度较大的m/z作为子离子,其中丰度最高的子离子作为定量离子,同时根据响应强弱选择适宜的碰撞能(CE),见表2。
表2 软骨藻酸母离子、子离子和碰撞能量
Tab.2
| 目标化合物 Compound | 母离子/(m/z) Parent ion | 子离子/(m/z) Daughter ion | 碰撞能量/eV Collision energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| DA | 312 | 266/*248 | 17/18 |
注:*为定量离子。
Note:*was quantitative ion.
2.2 色谱条件优化
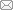
图1
图1
100 μg/L 软骨藻酸总离子流图
注:A.流动相A为甲醇溶液、流动相B为2 mmol/L乙酸铵缓冲溶液(含0.1%甲酸);B.流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液、流动相B为0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液。
Fig.1
Total ion flow diagram of 100 μg/L domoic acid
Notes:A.Mobile phase A was methanol,mobile phase B was 2 mmol/L ammonium acetate with 0.1% formic acid.B.Mobile phase A was water with 0.1% formic acid,mobile phase B was acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid.
2.3 净化条件优化
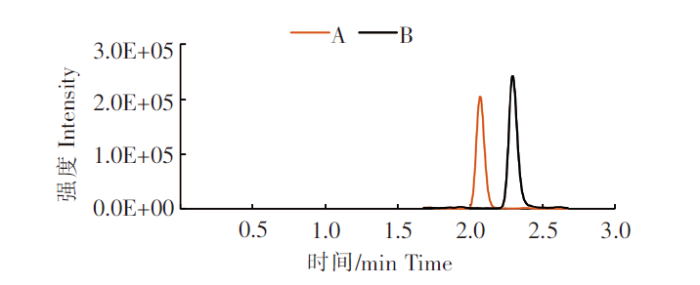
图2
图2
牡蛎中含80 μg/kg DA 两种固相萃取柱净化后总离子流图
注:A.SAX固相萃取柱净化;B.MAX固相萃取柱净化。
Fig.2
Total ion flow diagram of oyster containing 80 μg/kg DA after purification with two spe columns
Notes:A.SAX solid phase extraction column purification;B.MAX solid phase extraction column purification.
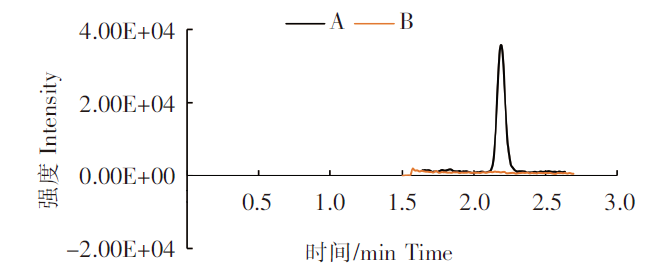
在确定DA仍吸附在MAX固相萃取柱上后,分别考察了0.3%甲酸溶液、1.0%甲酸溶液和5.0%甲酸甲醇溶液作为洗脱液的洗脱效果,如图3所示。HPLC-MS/MS检测发现,5.0%甲酸甲醇溶液作为洗脱液时有目标峰出现,但回收率仅为10%左右;另外两种洗脱液均未发现目标峰。
图3
图3
牡蛎中含80 μg/kg DA 三种洗脱液净化后总离子流图
注:A.0.3%甲酸溶液洗脱;B.1.0%甲酸溶液;C.5.0%甲酸甲醇溶液。
Fig.3
Total ion flow diagram after purification of three eluents containing 80 μg/kg DA in oyster
Notes:A.0.3% formic acid solution elution;B.1.0% formic acid solution;C.5.0% formic acid methanol solution.
因此,选择SAX固相萃取柱进行净化;洗脱液酸性较强,会对质谱产生一定影响,因而选择0.3%甲酸溶液作为洗脱液。
2.4 基质效应、线性范围和检出限
本研究中基质效应为-3.4%,DA的响应信号略微降低,属于弱基质效应。为减少基质效应带来的影响,采用空白基质液配制DA标准系列工作液,外标法定量测定。
以目标化合物的浓度为横坐标(x),定量离子的峰面积响应值为纵坐标(y)进行线性回归分析。在0.5~25.0 μg/L范围内线性关系良好,相关系数(R2)大于0.998,结果见表3。根据信噪比(S/N)≥3和信噪比(S/N)≥10计算检出限(LOD)为1.5 μg/kg,定量限(LOQ)为5 μg/kg。
表3 DA线性范围、线性方程及相关系数
Tab.3
| 目标化合物 Components | 线性范围/(μg/L) Linear range | 线性方程 Linear equation | 相关系数 R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DA | 0.5~25.0 | y=5 767.153x+1 891.442 | 0.998 |
2.5 准确度和精密度
DA的加标回收率和精密度实验结果如表4所示。DA在3个浓度水平的平均回收率为68.7%~92.4%,日内相对标准偏差在5.4%~8.4%之间(n=6),日间相对标准偏差在3.9%~5.1%之间(n=6),满足分析要求。
表4 加标回收率和精密度(n=6)
Tab.4
| 组分 Components | 添加水平/(μg/kg) Added level | 平均回收率/% Average recovery | 相对标准偏差/% RSD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日内 Intra day | 日间 Inter day | |||
| DA | 5.0 | 78.8 | 5.4 | 4.2 |
| 12.5 | 92.4 | 5.8 | 3.9 | |
| 50.0 | 68.7 | 8.4 | 5.1 | |
2.6 方法应用
本研究通过HPLC-MS/MS对福州、宁德和莆田3个福建省沿海重点养殖区的136个贝类样品进行DA检测分析,包括牡蛎、缢蛏、贻贝、花蛤、鲍、扇贝6种贝类,检测阳性样品结果见表5。检出DA的样品有27个,检出率为19.9%,检出含量在5.2~406.4 μg/kg之间,未超过欧盟安全标准20 mg/kg。
表5 阳性样品的DA含量
Tab.5
| 时间 Time | 样品名称 Sample name | 地点 Place | 含量/(μg/kg) Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-05 | 牡蛎 | 福州市福清市 | 38.4 |
| 2020-05 | 牡蛎 | 福州市连江县 | 10.8 |
| 2020-05 | 牡蛎 | 福州市连江县 | 10.4 |
| 2020-05 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市福安市 | 39.9 |
| 2020-05 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市福安市 | 28.2 |
| 2020-05 | 贻贝 | 宁德市福鼎市 | 25.9 |
| 2021-05 | 牡蛎 | 福州市罗源县 | 5.2 |
| 2021-05 | 牡蛎 | 福州市罗源县 | 16.1 |
| 2021-05 | 贻贝 | 宁德市福鼎市 | 12.9 |
| 2021-05 | 贻贝 | 宁德市霞浦县 | 7.1 |
| 2021-06 | 花蛤 | 福州市长乐区 | 127.6 |
| 2021-06 | 花蛤 | 福州市长乐区 | 98.8 |
| 2021-06 | 花蛤 | 福州市长乐区 | 44.9 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 福州市连江县 | 98.9 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 福州市连江县 | 86.5 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 莆田市北岸区 | 24.0 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 莆田市北岸区 | 10.3 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 莆田市北岸区 | 19.2 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 莆田市北岸区 | 33.3 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 莆田市北岸区 | 17.4 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市福鼎市 | 57.9 |
| 2021-06 | 贻贝 | 宁德市福鼎市 | 406.4 |
| 2021-06 | 贻贝 | 宁德市霞浦县 | 26.9 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市蕉城区 | 19.3 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市蕉城区 | 18.5 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市福鼎市 | 35.5 |
| 2021-06 | 牡蛎 | 宁德市霞浦县 | 17.9 |
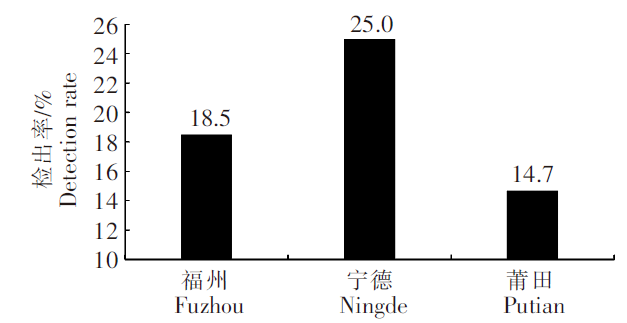
2.6.1 检出DA的地理分布
图4
图4
福州、宁德和莆田DA 检出率情况
Fig.4
Domoic acid detection rates in Fuzhou,Ningde and Putian
图5
图5
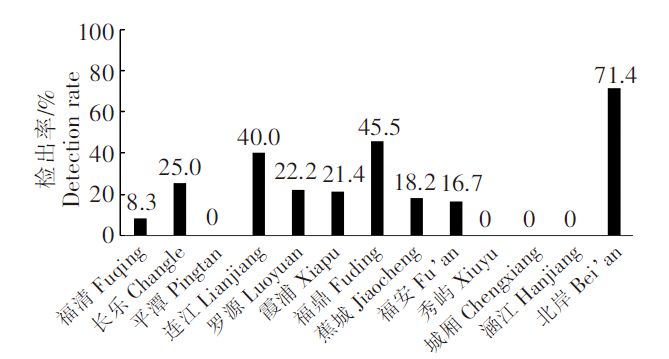
13 个县(市、区)DA 检出率情况
Fig.5
Detection rate of domoic acid in 13 counties(cities and districts)
2.6.2 检出DA的时间分布
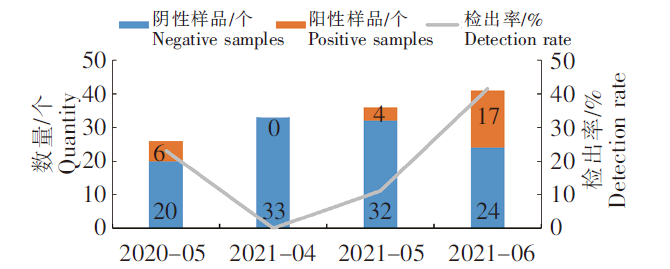
采集的136个贝类样品中,2020年5月采集的有26个,2021年4月有33个,2021年5月有36个,2021年6月有41个。2021年5月检出率为11.1%,比上年同期减少10%。2021年4—6月检出率呈逐渐递增趋势(0%~41.5%),见图6。
图6
2.6.3 检出DA的品种差异
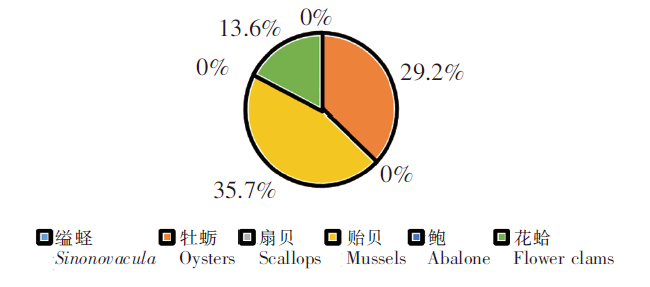
采集的136个样品中包括牡蛎、缢蛏、贻贝、花蛤、鲍、扇贝6种贝类。由图7可知,DA主要在花蛤、牡蛎和贻贝中检出,检出率为13.6%~35.7%;缢蛏、鲍和扇贝中均未检出DA。
图7
3 讨论
福建省仅2012年至2018年7月就发生赤潮56起[25],赤潮的频繁暴发,导致我省海域养殖贝类受到不同程度的污染,贝类毒素中毒事件屡次发生:如2011年6月宁德市福鼎、霞浦等地发生震惊全国的食用贻贝中毒事件,造成168人中毒;2014年6月至7月,福州罗源、漳州等地发生织纹螺中毒事件;2015年6月,福建莆田发生织纹螺中毒事件,致使2岁男童留下严重的神经系统后遗症等[26];2017年漳州、泉州海域发生有毒链状裸甲藻(Gymnodinium catenatum)赤潮,致使赤潮影响海域滤食性贝类麻痹性贝毒(Paralytic shellfish poison,PSP)超标,造成多地民众因食用滤食性贝类而发生中毒事件[27]。在这种形势下,对贝类毒素的分析研究越来越重要。
由于受仪器设备的限制,国家还未颁布使用HPLC-MS/MS法检测贝类中失忆性贝类毒素的标准。本研究参照GB 5009.198—2016《食品安全国家标准 贝类中失忆性贝类毒素的测定》,并结合HPLC-MS/MS技术,建立了检测贝类体内DA残留的方法。通过对净化条件的改进、色谱条件和质谱条件的优化,有效解决了样品中杂质对DA检测的影响。DA在0.5~25.0 μg/L范围内线性关系良好,相关系数(R2)大于0.998,检出限(LOD)为1.5 μg/kg,定量限(LOQ)为5 μg/kg。在5.0、12.5、50.0 μg/kg 3个浓度水平下的平均回收率为68.7%~92.4%,日内相对标准偏差在5.4%~8.4%之间(n=6),日间相对标准偏差在3.9%~5.1%之间(n=6)。LC-MS法DA检出限为3 μg/kg,定量限为10 μg/kg[19],而本文建立的HPLC-MS/MS方法比常规LC-MS法的进样量低5倍,且灵敏度高2倍,能够有效减少对仪器的污染,更好地净化贝类样品中的脂肪、蛋白质等杂质,消除基质效应,具有快速、高效、高灵敏度和高准确度等优点。
运用建立的方法对福州、宁德、莆田3个重点海域的136个贝类样品进行DA检测。分析发现福建贝类中DA含量总体水平较低,但仍有少量检出,主要在花蛤、牡蛎和贻贝中,含量在5.2~406.4 μg/kg之间,检出率为13.6%~35.7%。有研究表明,通常情况下温度升高会促使更多DA的产生。比如成列拟菱形藻(P.seriata)在4~15℃范围内、多列拟菱形藻(P.australis)在5~25℃范围内、澳洲拟菱形藻在23~30℃范围内,DA的产量会随温度的升高而有所增加[28],这与本研究2021年4—6月检出率呈逐渐递增趋势(0%~41.5%)检测结果一致。从现有文献报道来看,贝类中存在一定水平的毒素污染。吉薇等从11批次样品中检出9批次有DA积累,检出率为81.8%,其中钝齿短桨蟹中DA含量为18.2 mg/kg,已接近欧盟安全标准[29]。陈西平等在14个批次样品中检出7个样品含有DA,含量在 0.4~8.1 mg/kg,检出率达50%[30]。王恒对采集的13种贝类共39份样品检测,DA检出率为64%[31]。因此要加强对贝类中DA的监测,为我国统一DA安全标准的制定提供参考。
本方法检测低限达到5 μg/kg,且线性关系良好,满足欧盟规定的DA 20 mg/kg安全标准,适用于贝类中DA的日常检测和监控,为相关部门强化贝类质量安全监管、加强贝类风险管控、推动贝类产业健康可持续发展提供参考依据。
参考文献
Identification of domoic acid,a neuroexcitatory amino acid,in toxic mussels from eastern Prince Edward Island
[J].
An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid
[J].In Canada in late 1987 there was an outbreak of an acute illness characterized by gastrointestinal symptoms and unusual neurologic abnormalities among persons who had eaten cultivated mussels. Health departments in Canada solicited reports of this newly recognized illness. A case was defined as the occurrence of gastrointestinal symptoms within 24 hours or of neurologic symptoms within 48 hours of the ingestion of mussels. From the more than 250 reports received, 107 patients met the case definition. The most common symptoms were vomiting (in 76 percent of the patients), abdominal cramps (50 percent), diarrhea (42 percent), headache, often described as incapacitating (43 percent), and loss of short-term memory (25 percent). Nineteen patients were hospitalized, of whom 12 required intensive care because of seizures, coma, profuse respiratory secretions, or unstable blood pressure. Male sex and increasing age were associated independently with the risks of hospitalization and memory loss. Three patients died. Mussels associated with this illness were traced to cultivation beds in three river estuaries on the eastern coast of Prince Edward Island. Domoic acid, which can act as an excitatory neurotransmitter, was identified in mussels left uneaten by the patients and in mussels sampled from these estuaries. The source of the domoic acid appears to have been a form of marine vegetation, Nitzschia pungens, also identified in these waters in late 1987. The contaminated mussels from Prince Edward Island were removed from the market, and no new cases have occurred since December 1987. We conclude that the cause of this outbreak of a novel and severe intoxication was the ingestion of mussels contaminated by domoic acid, a potent excitatory neurotransmitter.
Domoic acid as a developmental neurotoxin
[J].Domoic acid (DomA) is an excitatory amino acid which can accumulate in shellfish and finfish under certain environmental conditions. DomA is a potent neurotoxin. In humans and in non-human primates, oral exposure to a few mg/kg DomA elicits gastrointestinal effects, while slightly higher doses cause neurological symptoms, seizures, memory impairment, and limbic system degeneration. In rodents, which appear to be less sensitive than humans or non-human primates, oral doses cause behavioral abnormalities (e.g. hindlimb scratching), followed by seizures and hippocampal degeneration. Similar effects are also seen in other species (from sea lions to zebrafish), indicating that DomA exerts similar neurotoxic effects across species. The neurotoxicity of DomA is ascribed to its ability to interact and activate the AMPA/KA receptors, a subfamily of receptors for the neuroexcitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. Studies exploring the neurotoxic effects of DomA on the developing nervous system indicate that DomA elicits similar behavioral, biochemical and morphological effects as in adult animals. However, most importantly, developmental neurotoxicity is seen at doses of DomA that are one to two orders of magnitude lower than those exerting neurotoxicity in adults. This difference may be due to toxicokinetic and/or toxicodynamic differences. Estimated safe doses may be exceeded in adults by high consumption of shellfish contaminated with DomA at the current limit of 20 microg/g. Given the potential higher susceptibility of the young to DomA neurotoxicity, additional studies investigating exposure to, and effects of this neurotoxin during brain development are warranted.Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Ion-spray mass spectrometry of marine neurotoxins
[J].Ion-spray mass spectrometry was investigated for the analysis of three marine neurotoxins: domoic acid, saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin. All three compounds gave positive-ion spectra with abundant ions of protonated molecules and no significant fragmentation. Domoic acid gave a negative-ion spectrum with a strong [M-H]- ion. Tandem mass spectrometry provided useful fragment-ion spectra for all compounds. Detection limits for flow injection analyses with selected-ion monitoring were determined to be 30 pg for saxitoxin, 100 pg for domoic acid and 200 pg for tetrodotoxin. Combining liquid chromatography with ion-spray mass spectrometry allowed the determination of domoic acid and some of its isomers in toxic shellfish tissue extracts.
Determination of domoic acid in shellfish by liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization and multiple tandem mass spectrometry
[J].Amnesic shellfish poisoning is a potentially lethal human toxic syndrome which is caused by domoic acid (DA) that originates in marine phytoplankton belonging to the Pseudonitzschia genus. A new sensitive liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) method has been developed for the determination of DA in various marine biological samples. The characteristic fragmentation pathways for DA were established using multiple stage MS on selected daughter ions, which were sequentially trapped and fragmented. Chromatography was performed using a gradient of acetonitrile-water (5:95 to 40:60), containing trifluoroacetic acid (0.05%), over 25 min at 0.2 ml/min with a C18 column (Luna-2, 150 x 2.0 mm, 5 microm). Using electrospray ionisation, multiple tandem MS experiments were performed with an ion-trap mass spectrometer (Finnigan MAT LCQ). The protonated DA molecule was the precursor ion, m/z 312, and the relative collision energies were optimised for multiple MS (MS(n), n = 2-4) studies. LC-MS3 using the ions, m/z 266 and 220, from the loss of two HCOOH molecules, produced the best sensitivity data. Calibration data for various MS modes were: MS (0.05-10 microg DA/ml, r2 = 0.9973); MS2 (0.025-10 microg DA/ml, r2=0.9997); MS3 (0.025-10 microg DA/ml, 0.9994). The detection limits (3:1 signal:noise) were better than 0.02 microg DA/ml for LC-MS, 0.014 microg DA/ml for LC-MS2 and 0.008 microg DA/ml for LC-MS3. This method was applied to determine DA in scallop (Pecten maximus) tissues, which subsequently led to the closure of several shellfish harvesting sites on the west coast of Ireland.
Determination and confirmation of the amnesic shellfish poisoning toxin,domoic acid,in shellfish from Scotland by liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
[J].During 1998 and early 1999, shellfish samples from sites in Scotland were found to contain the amnesic shellfish poisoning toxin, domoic acid (DA). Two different techniques, liquid chromatography (LC) with UV diode-array detection and LC with mass spectrometric (MS) detection, were used to detect and confirm DA in shellfish extracts. The LC/UV method was validated for routine monitoring by recovery experiments on spiked mussel and scallop tissues with a certified mussel tissue used as reference material. Crude extracts of selected samples as well as extracts cleaned with strong anion exchange (SAX) were analyzed by both LC/UV and LC/MS. Good correlation (linear regression r2 = 0.996, slope = 0.93) between the 2 methods was found for cleaned extracts. Analyses of crude extracts by LC/UV produced false-positive results in 2 crab samples, whereas LC/MS analyses gave accurate results. It was concluded that LC/UV is a valid approach for routine monitoring of DA in shellfish when cleanup is performed with a SAX cartridge to prevent false positives. A variety of shellfish species were surveyed for DA content, including Pecten maximus (king scallops), Chlamys opercularis (queen scallop), Mytilus edulis (blue mussels), Cancer pugaris (crab), and Ensis ensis (razor fish). The highest concentration of DA was 105 microg/g in Pecten maximus.
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for determination of domoic acid in Adriatic shellfish
[J].This paper describes a new method for sensitive, specific and direct determination of domoic acid (DA), the causative toxin of amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) syndrome, in shellfish. It is based on combination of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry (HILIC/MS). The high percentage of organic modifier in the mobile phase and the omission of ion-pairing reagents, both favoured in HILIC, result in enhanced detection limits with MS detection. The new method was set up either on an ionspray ion trap MS instrument operating in MS and MS/MS scanning acquisition modes, or on a turboionspray triple-quadrupole MS system operating in selected ion monitoring (SIM) and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) acquisition modes. Positive and negative ion experiments were performed. MRM experiments are recommended for screening contaminated shellfish tissue and for quantitative analyses due to highest sensitivity and selectivity. The minimum detection levels for the toxin in tissue were found to be 63 and 190 ng/g in positive and negative MRM experiments, respectively, which are well below the regulatory limit for DA in tissue (20 microg/g). Application to shellfish samples collected in the Adriatic Sea (Italy) in the period 2000-2004 demonstrated for the first time in Italy the presence of DA as a new toxin that has entered the Adriatic Mytilus galloprovincialis toxin profile.Copyright (c) 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Screening for multiple classes of marine biotoxins by liquid chrom atography-high-resolution mass spectrometry
[J].
免疫亲和柱净化-高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱法测定双壳类水产中软骨藻酸
[J].
液相色谱-串联质谱生物分析方法的基质效应和对策
[J].液相色谱-串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)法具有高灵敏度、高选择性、高通量等特点,已经成为生物分析的主流方法,广泛应用于新药发现和开发过程中新化学实体及其代谢物的定量分析。然而,由于生物样品基质成分复杂,共洗脱物质会影响分析物的离子化,使分析物的质谱响应增加或降低,从而影响LC-MS/MS分析方法的准确度和精密度。一般而言,离子抑制较离子增强更为常见。因此,在建立LC-MS/MS法时,需要对离子抑制进行评估和校正,并采用不同的策略消除或减少基质效应的影响。本文综述了生物样品分析中基质效应的来源和评估方法,重点介绍了克服基质效应的策略。引起基质效应的物质包括磷脂、盐类、尿素、代谢物等内源性物质和赋形剂、抗凝剂、固定相释放物质及降解产物等外源性物质。目前基质效应的评价方法主要有提取后加入法和柱后灌注法。克服基质效应的策略主要有使用稳定同位素内标,将极性药物衍生化,沉淀蛋白后稀释上清液,优化样品预处理方法、色谱和质谱条件等。结合本课题组的应用实例,重点阐述了建立LC-MS/MS生物分析方法时,为减少基质效应遇到的困难及解决方法。
全自动固相萃取-超高效液相色谱法测定淡水养殖水体中的呋喃丹
[J].本文建立了淡水养殖水体中呋喃丹的全自动固相萃取-超高效液相色谱检测方法。选取HLB固相萃取小柱作为水样的富集和净化小柱,水样以5 mL·min-1的速度上样,用10 mL甲醇洗脱。洗脱液经浓缩、定容后,用超高效液相色谱-荧光检测法分析,色谱柱为ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18柱(100 mm × 2.1 mm,粒径1.7 μm),流动相为乙腈-水(40∶60,V/V),流速为0.200 mL·min-1,激发波长为270 nm,发射波长为310 nm。呋喃丹在20~1 000 μg·L-1范围内线性关系良好,相关系数R2 > 0.999,方法检出限为0.100 μg·L-1,定量限为0.250 μg·L-1,在0.250、2.50、10.0 μg·L-1三种加标浓度水平下,平均加标回收率为90.4% ~ 96.3%,相对标准偏差为2.55% ~ 5.10%。该方法自动化程度高、操作简便、快速准确、稳定性好,适用于淡水养殖水体中呋喃丹的测定。
HPLC-MS/MS法检测福建中部海域养殖贝类麻痹性贝类毒素
[J].实验采用高效液相色谱-串联质谱法(HPLC-MS/MS)检测2017—2018年福建中部海域养殖贝类麻痹性贝类毒素(PSTs)。结果表明:2018年采集的贝类样本均未检出麻痹性贝类毒素,2017年采集的贝类样本有17批次检出麻痹性贝类毒素,主要检出成分为脱氨甲酰基石房蛤毒素(dcSTX)、膝沟藻毒素(GTX1、GTX2、GTX3、GTX4、GTX5),脱氨甲酰基膝沟藻毒素(dcGTX2、dcGTX3)也占有一定比例,未发现石房蛤毒素(STX)。2017年福建中部海域链状裸甲藻(Gymnodinium catenatum)暴发事件对该海域养殖贝类的麻痹性贝类毒素有一定影响,其中有毒赤潮对贻贝的影响大于牡蛎,而对缢蛏和蛤类则无影响。
2017年福建海域链状裸甲藻赤潮事件应急处置与思考
[J].福建是我国赤潮多发省份之一,2000—2017年共发现赤潮219起,其中35起赤潮造成养殖损失或群众健康受损事件。做好有毒赤潮应急处置,对保障人民群众生命安全,维护海洋渔业经济健康发展,服务福建生态省建设至关重要。本文以2017年福建中南部沿海海域链状裸甲藻赤潮事件为例,对赤潮事件过程、主要应急处置措施、存在的问题进行分析与讨论。在此次有毒赤潮事件处置过程中,政府部门采取及时控制贝毒超标水产品养殖区源头、根据赤潮动态调整监视监测工作、主动公开赤潮有关情况、适时终止应急响应等措施,有效地遏制赤潮对社会和水产品质量安全等不利影响的进一步扩大,切实保障群众水产品食用安全及生命财产的安全。针对事件过程中暴露出部门联动、赤潮监测能力等方面的不足,提出完善协同应急响应机制、加强地市级基本应急能力建设、利用新技术开展有毒赤潮生物监测、推广快检技术以加强海水贝类质量安全监测等建议。