鲂属(Magalobrame)鱼类,在分类地位上属于鲤形目(Cypriniformes)、鲤科(Cyprinidae)和鲌亚科(Cultrinae),该属主要包括4种鱼类:三角鲂(Megalobrama terminalis)、团头鲂(M.amblycephala)、广东鲂(M.hoffmanni)和厚颌鲂(M.pellegrini)等。团头鲂,又名“武昌鱼”,是我国特有的优良草食性鱼类,因食性广、生长快、养殖成本低等优点,其还是我国主要的大宗淡水水产养殖品种之一[1]。三角鲂,在钱塘江附近地区被称为“三角鳊”“塔鳊”,在黑龙江附近地区被称为“法罗”。相对于团头鲂,三角鲂的养殖区域较小,但因具有快速生长期长、商品个体大等特点,三角鲂在浙江、湖南、山东、江苏等地也具有一定的养殖规模,具有良好的养殖前景[2-3]。
近年来,团头鲂病害频发,由嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)引起的细菌性败血症是团头鲂养殖过程中危害较大的疾病之一,严重影响养殖效益[4]。而养殖实践发现,与同属的团头鲂相比,三角鲂的细菌性败血症发生率较低,即使发生了该病,使用常规药物就可较好地控制,未有大面积发病的情况,且病死率低。三角鲂和团头鲂之间差异小,亲缘关系较近[5],但2种鱼类在感染嗜水气单胞菌后所表现出的差异,除去环境因素外,遗传因素是其中一个重要的原因。此前,方献平等[6]采用非标记定量蛋白质组学技术分析了在嗜水气单胞菌侵染胁迫后3 h、10 h和24 h肝组织蛋白质组的变化,结果表明三角鲂在戊糖磷酸途径、脂肪酸代谢、亮氨酸降解等通路与团头鲂存在显著差异。为在基因组注释的丰富度以及期望于基因水平上了解三角鲂和团头鲂在嗜水气单胞菌侵染过程中的表达差异,本文基于转录组测序技术研究了三角鲂和团头鲂在感染嗜水气单胞菌后转录组的变化,以期了解三角鲂和团头鲂在嗜水气单胞菌感染上的差异性,为阐明嗜水气单胞菌致病机制乃至抗病育种提供研究基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
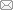
实验用三角鲂和团头鲂由杭州市农业科学研究院水产研究所提供,嗜水气单胞菌株分离自江苏武进某养殖场。致病实验与方献平等[6]报道实验相同,选取了3 h和24 h两个时间点,每个时间点分别取三角鲂和团头鲂各5尾,体质量为130.5~150.5 g。每5尾鱼分别取肌肉、肝脏、血液3个组织并分别浸泡于3份RNAfixer无液氮RNA样品储存液中,于-80℃冰箱中保存备用。测序时,每3个组织等质量混合后作为1份实验材料,进行建库和测序。各实验样品被分别标记为SJF3、SJF20、TTF3、TTF20,表示3 h和24 h两个时间点采集的三角鲂和团头鲂样品。
1.2 RNA提取及建库测序
RNA提取及建库测序委托杭州英睿生物科技有限公司完成。取总RNA样品,利用试剂盒合成cDNA,通过末端修复、连接接头和纯化,获得三角鲂和团头鲂的cDNA文库,建好的文库通过Illumina HiseqTM 2000平台进行测序。测序样本的原始数据(Raw Reads)过滤与组装等步骤参照刘凯等[7]的方法进行,过滤数据时,采用Cutadapt去除3'端带接头的序列以及去除平均质量分数低于Q20的Reads,使用Trinity软件对所有样本的Clean Reads进行拼接,最终组装获得Unigenes,作为参考序列。
1.3 功能注释、分类及代谢途径分析
通过blastx、Blast2GO和KOBAS等程序将Unigenes比对到数据库NR(NCBI non-redundant protein sequences)、COG(Cluster of orthologous groups of proteins)、GO(Gene ontology)和KEGG(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)等,进而得到Unigenes的功能注释信息。
1.4 差异基因分析
图1
2 结果与分析
2.1 转录组数据与组装
表1 测序数据质量评估
Tab.1
| 样品 Sample | 原始测序数据量 Raw Reads | 原始测序数据大小 Raw bases | 有效测序数据量 Clean Reads | 有效测序数据大小 Clean bases | 有效比例/% Clean data rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJF20 | 29 209 630 | 4 381 444 500 | 29 208 858 | 4 353 671 917 | 99.997 4 |
| SJF3 | 28 563 714 | 4 284 557 100 | 28 562 552 | 4 250 964 033 | 99.995 9 |
| TTF20 | 28 372 598 | 4 255 889 700 | 28 371 800 | 4 226 829 069 | 99.997 2 |
| TTF3 | 28 681 776 | 4 302 266 400 | 28 680 944 | 4 270 279 163 | 99.997 1 |
表2 测序数据的统计汇总
Tab.2
| 数据整合Assembly | 统计分析Summary statistics |
|---|---|
| 基因数量Unigene number | 62 780 |
| 最大基因碱基数Max Unigene bases | 15 579 |
| 最小基因碱基数Min Unigene bases | 200 |
| 总数据集长度Whole dataset lengths | 33 391 666 |
| 基因平均长度/bp Average Unigene lengths | 531.883 |
| GC含量/% GC content | 45.7 |
| N50 | 652 |
| N90 | 237 |
2.2 转录组功能注释
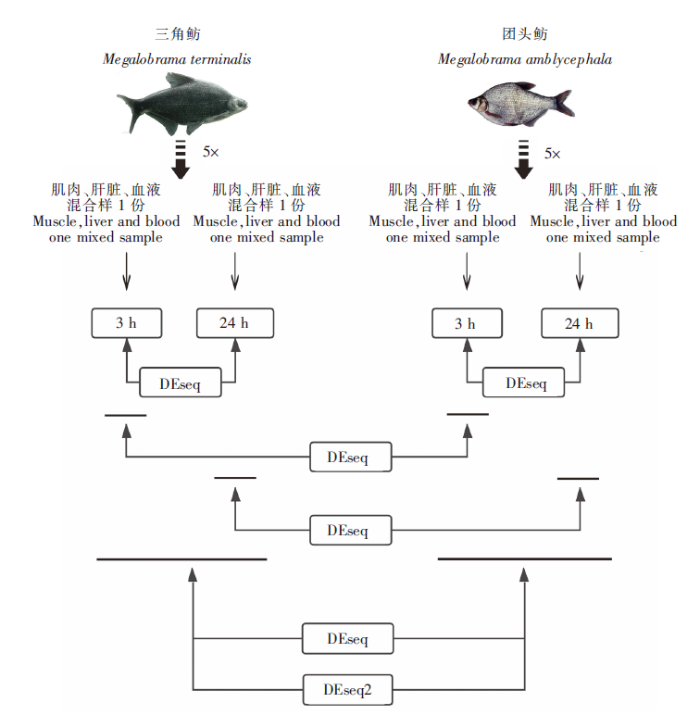
在拼接获得Unigenes后,与公共数据库进行比对注释,62 780个Unigenes中有35 443个可注释到NR数据库,比例最高,为56.46%;仅有8 632个可注释到COG数据库,比例最低,为13.75%(表3)。在NR数据库注释中,注释来源最多物种为斑马鱼(Danio rerio),其次为鲢鱼(Hypophthalmichthys molitrix)、鳙鱼(Hypophthalmichthys nobilis)等(图2)。在GO数据库注释中,11 622个Unigenes被注释到38个GO Term分类上,其中生物学过程GO Term分类的相关基因较多,如GO:0009987 细胞过程GO Term分类上注释了4 599个Unigenes;分子功能GO Term分类中,GO:0005488 细胞结合GO Term分类相关基因最多,注释了7 413个Unigenes。在COG数据库注释中,一般功能预测分类注释的Unigenes最多,为1 979个;其次为翻译后修饰、蛋白质周转、伴侣的分类,注释Unigenes 1 353个;之后为转录分类,注释Unigenes 684个。在KEGG数据库注释中,注释Unigenes 最多的前3个通路分别是补体和凝血级联、金黄色葡萄球菌感染、吞噬体,注释Unigenes 达到9 898、3 721和1 653个。
表3 基因注释结果统计
Tab.3
| 数据库Database | 基因总数Total Unigenes | 注释基因数Annotated Unigenes | 注释比例/% Annotated percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 62 780 | 35 443 | 56.46 |
| GO | 62 780 | 11 622 | 18.51 |
| COG | 62 780 | 8 632 | 13.75 |
| KEGG | 62 780 | 18 213 | 29.01 |
图2
图2
NR 数据库注释物种分布图
Fig.2
Taxonomy statistics result of Unigenes annotation in NR database
2.3 基因表达的差异分析
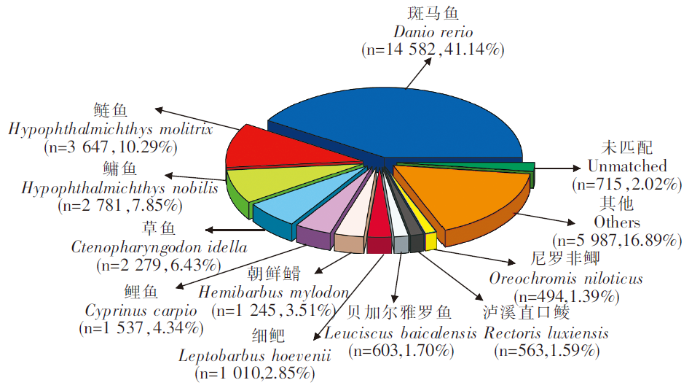
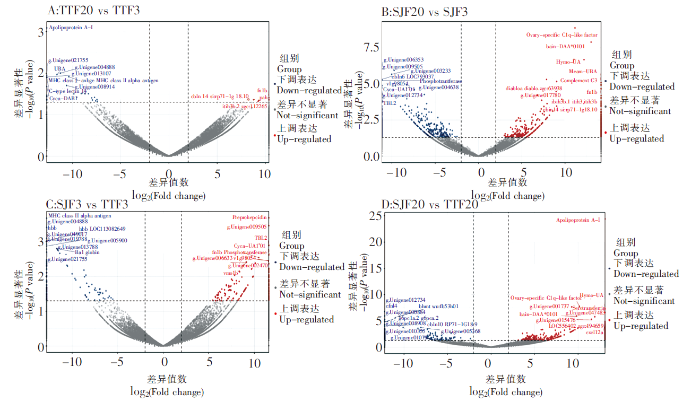
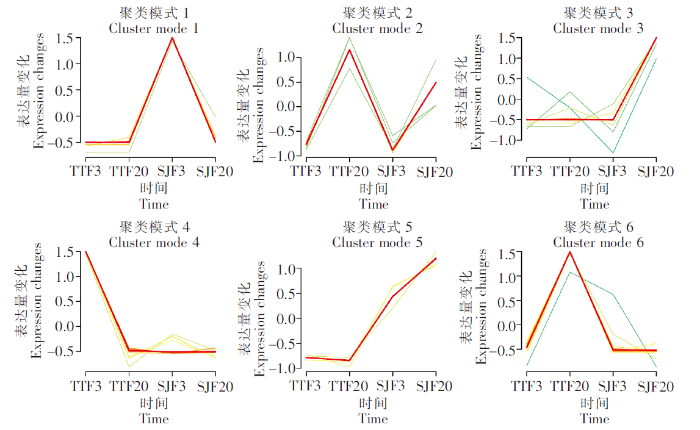
62 780个Unigenes中,有33 693个Unigenes在三角鲂中表达,有32 936个Unigenes在团头鲂中表达,其中有24 834个Unigenes在三角鲂和团头鲂中共表达。基于DESeq,分别比较了三角鲂、团头鲂在3 h和24 h时间点上基因表达的差异变化(图3)。对TTF20-TTF3的差异分析表明,团头鲂感染24 h后与感染3 h后相比,显著上调表达的基因有4个,分别为FN1b、PAH、CBLN14和INIH3b.2,显著下调表达基因的前10个主要有Apolipoprotein A-I、C-type lectin 14以及UBA、MHC classⅠ antigin和MHC classⅡ alpha antigen等。对SJF20-SJF3的差异分析表明,三角鲂感染24 h后与感染3 h后相比,显著上调表达的基因的前10个主要有Ovary-specific C1q-like factor、Complement C3以及bain-DAA*0101、Hymo-UA和Meam-UBA等主要组织相容性复合物(Major histocompatibility complexes,MHC)相关基因,显著下调表达基因的前10个主要有CBLN6 LOC793037、Phosphotransferase、TBL2和Cyca-UA1*01等。对SJF3-TTF3的差异分析表明,在感染3 h后,三角鲂相对于团头鲂,显著上调表达的基因的前10个主要有Preprohepcidin、FN1b、TBL2、Phosphotransferase和Cyca-UA1*01等,显著下调表达基因的前10个主要有MHC classⅡ alpha antigen、HBB、HBB LOC113082649和Ba1 globin等。对SJF20-TTF20的差异分析表明,在感染24 h后,三角鲂相对于团头鲂,显著上调表达的基因的前10个主要有Apolipoprotein A-I、Ovary-specific C1q-like factor、Serotransferrin、Hymo-UA和bain-DAA*0101等,显著下调表达基因的前10个主要有CFHL4、BHMT wu:fb53h01、G6PC1a.2和CBLN10 RP71-1G18.9等。将以上显著上调或下调表达的基因进行表达趋势聚类分析(图4),三角鲂、团头鲂在3 h和24 h时间点上基因表达趋势可划分为6类,其中聚类模式4所包含的差异表达基因最多,为16个;聚类模式1所包含的差异表达基因数量为15个;聚类模式6包含基因12个;聚类模式3包含基因10个;聚类模式2、5分别包含基因5个、4个。由此可见,三角鲂、团头鲂基因表达趋势聚类主要模式为4、1、6和3。从以上主要聚类模式可见,三角鲂、团头鲂之间差异表达的基因主要以三角鲂或团头鲂下调表达的较多,而上调表达的基因较少。
图3
图3
基于DESeq 分析团头鲂和三角鲂不同时间点的差异基因
注:红色点表示显著上调的基因,其中显著上调的前10个基因标注了基因名。蓝色点表示显著下调的基因,其中显著下调的前10个基因标注了基因名。
Fig.3
Differential genes analysis of Megalobrama amblycephala and Megalobrama terminalis at different time points based on DESeq
Notes:Red dots indicated significantly up-regulated genes,where the top 10 significantly up-regulated genes were labeled with gene names.Blue dots indicated significantly down-regulated genes,where the top 10 significantly down-regulated genes were labeled with gene names.
图4
图4
基于DESeq 分析的差异基因表达趋势聚类
注:不同颜色线表示基于DESeq分析的差异基因在不同时间点和样本之间的表达变化。
Fig.4
Clustering of differential gene expression trend based on DESeq
Note:The different colored lines indicated the variation in expression of differential genes based on DESeq analysis across time points and samples.
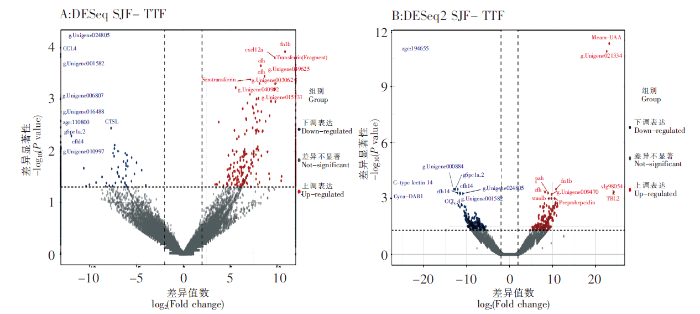
基于DESeq和DESeq2,从总体上比较了三角鲂相对于团头鲂基因表达的差异变化(图5)。基于DESeq对SJF-TTF的差异分析表明,显著上调表达的基因的前10个主要有FN1b、CXCL12a、CFH、Transferrin(Fragment)和Serotransferrin等,显著下调表达基因的前10个主要有CCL4、CFHL4、G6PC1a.2和CTSL等。基于DESeq2对SJF-TTF的差异分析表明,显著上调表达基因的前10个主要有Meam-UAA、TBL2、CFH、PAH、FN1b和Preprohepcidin等,显著下调表达基因的前10个主要有Cyca-DAB1、CFHL4、C-type lectin 14、G6PC1a.2和CCL4等。比较DESeq和DESeq2分析结果发现,有7个差异表达的基因在DESeq和DESeq2中均被鉴别出来,分别是上调表达基因FN1b和CFH,下调表达基因CCL4、CFHL4、G6PC1a.2,以及2个未注释的基因g.Unigene024805和g.Unigene001582。
图5
图5
基于DESeq 和DESeq2 分析团头鲂和三角鲂的差异基因
Fig.5
Differential genes of Megalobrama amblycephala and Megalobrama terminalis based on DESeq and DESeq2
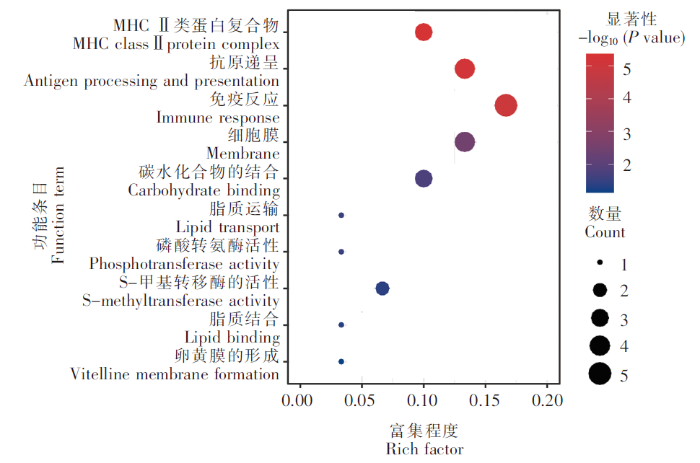
2.4 差异表达基因的富集分析
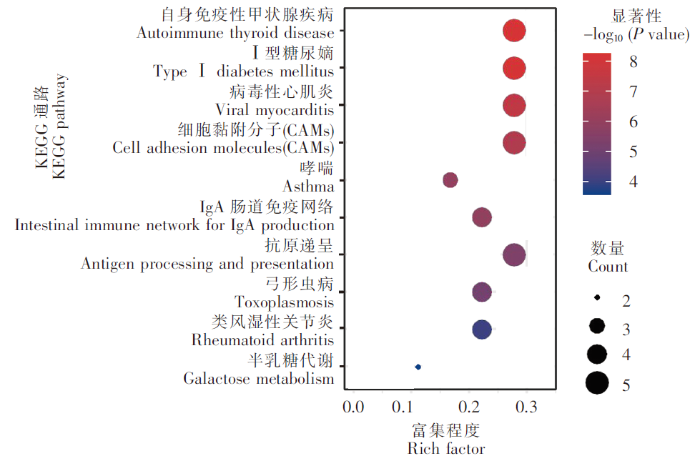
对基于DESeq和DESeq2方法分别获得的前20个表达差异最显著的基因进行GO富集分析,通过Rich factor、P value值和富集到GO Term上的基因个数来衡量富集的程度(图6)。其中,免疫反应(GO:0006955)条目下富集的差异表达基因最多,30个GO注释的差异基因中有5个差异基因在此条目下;其次为抗原递呈(GO:0019882)和细胞膜(GO:0016020)2个条目,以及MHCⅡ类蛋白复合物(GO:0042613)和碳水化合物结合(GO:0030246)等条目。以上结果表明,三角鲂和团头鲂之间的抗感染差异与抗原递呈相关基因关系密切。进一步对以上获得的差异表达基因进行KEGG富集分析,富集程度的表征与GO富集分析类似(图7)。其中,自身免疫性甲状腺疾病(ko05320)、Ⅰ型糖尿病(ko04940)、病毒性心肌炎(ko05416)、细胞黏附分子(ko04514)和抗原递呈(ko04612)5个KEGG通路是富集程度最高的,18个KEGG注释的差异基因中,均有5个基因富集在这些通路下。剩下的通路还包括IgA肠道免疫网络(ko04672)、弓形虫病(ko05145)和类风湿性关节炎(ko05323)等。综上,依然可见抗原递呈相关基因与三角鲂和团头鲂之间的抗感染差异有关,此外细胞黏附通路(ko04514)也与细菌感染密切相关。
图6
图6
差异表达基因GO 显著富集结果
Fig.6
The significantly enriched GO Term of differentially expressed genes
图7
图7
差异表达基因KEGG 通路显著富集结果
Fig.7
The significantly enriched KEGG pathway of differentially expressed genes
3 讨论
由于转录组测序无需事先以已知序列为目标,因此可以对任意物种进行测序而无需知道物种的基因组背景,这为研究物种间基因表达差异提供了方便[11-12]。因此,本研究基于转录组测序分析三角鲂和团头鲂抗嗜水气单胞菌感染的基因表达的差异。将三角鲂和团头鲂样本的测序数据经过滤后组装Unigenes作为参考序列,使用RSEM软件比对Unigenes序列确定表达量,以团头鲂为对照,分析三角鲂Unigenes表达量的相对变化。此前,方献平等[6]采用非标记定量蛋白质组学技术,分析在嗜水气单胞菌侵染胁迫后3 h、10 h和24 h时三角鲂和团头鲂肝组织蛋白质组的变化。基于方献平等[6]的蛋白应答聚类分析发现,10 h和24 h的应答蛋白质优选聚类后再与3 h的应答蛋白质聚类,表明10 h和24 h蛋白质应答具有相似性。基于此,本研究选择3 h和24 h作为时间节点开展转录组分析。由于方献平等[6]的分析仅基于肝脏组织,不能完全反映整个机体对嗜水气单胞菌侵染的应答情况。因此,本研究进一步分析了肌肉、肝脏和血液的混合组织样,以更全面了解三角鲂和团头鲂在抗嗜水气单胞菌侵染过程中基因表达的差异性。此外,由于DESeq2可以消除DESeq的边界效应,因此在进行整体分析中采用了DESeq2方法与DESeq方法共同进行了分析,减少单方法分析的误差。
基于DESeq的基因表达趋势聚类分析表明,三角鲂和团头鲂在3 h和24 h时间节点上的基因表达均表现为表达量无变化、表达上调和表达下调等3种情况,但其中主要以三角鲂表达量无变化、团头鲂表达下调(Cluster 4),团头鲂表达量无变化、三角鲂表达下调(Cluster 1)为主。可见,三角鲂、团头鲂之间差异表达的基因主要以三角鲂或团头鲂下调表达为主,这与罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)的情况类似[13],但与蛋白质组学分析结果存在差异[6]。此外,为从总体上评估三角鲂和团头鲂感染后基因表达差异,进一步基于DESeq和DESeq2方法进行了分析,并进一步鉴定出上调表达基因FN1b和CFH、下调表达基因CFHL4和CCL4等,提示以上基因表达与三角鲂和团头鲂的感染差异相关。FN1b是编码纤维连接蛋白(Fibronectin,FN)的两种基因亚型之一[14],纤维连接蛋白则是细胞外基质的重要成分之一,而细胞外基质被认为是影响器官形成与修复的关键因子[15]。CFH (Complement factor H)即补体因子H,调节血浆中补体的替代途径,抑制补体活性并介导细胞表面对替代途径激活剂和非激活剂的区分[16]。CFH蛋白产生缺陷后可致替代途径异常激活,导致细胞损伤[17]。CCL4[Chemokine(C-C motif)ligands 4 ]即CC型趋化因子配体4,是CC型趋化因子家族的一员,因其从脂多糖激活的巨噬细胞中被分离出来,亦称MIP-1β[18],它在免疫细胞迁移、活化、分化和增殖等方面具有重要作用[19]。三角鲂相对于团头鲂,FN1b和CFH基因表达显著上调,表明三角鲂在受到细菌攻击时更倾向于自我修复,而CCL4基因的下调,则表明团头鲂调动了更多的细胞因子用于消除细菌。CFHL4则是补体因子H相关蛋白(Complement factor H-related protein,FHRs)之一[16],目前关于其具体机制并未明确,但越来越多的数据表明,FHRs与CFH具有相反的作用,即它们直接增强补体活性[20]。因此,推测三角鲂相对于团头鲂CFHL4基因表达的下调也与三角鲂细胞自我修复基因有关。
基于GO和KEGG富集分析,对DESeq和DESeq2方法鉴定出的主要差异基因进行了富集分析,均表明三角鲂和团头鲂的感染差异与抗原递呈相关基因密切相关。基于转录组学对罗非鱼感染后的基因表达分析表明,吞噬作用在罗非鱼的抗感染免疫中起到重要作用,其中主要组织相容性复合物基因就是主要的吞噬相关基因[13]。本文结果与此类似,也确定了MHC基因在感染后的重要作用,并表明其与三角鲂和团头鲂抗感染差异相关。基于团头鲂MHCⅡα基因的研究也表明,MHC基因与团头鲂抗病性密切相关[21]。在DESeq和DESeq2共同鉴定出的差异基因中,仅FN1b被KEGG注释,其富集在ECM-受体相互作用(ko04512)通路(图7中未显示),表明ECM即细胞外基质与三角鲂和团头鲂抗感染差异密切相关。此外,在GO和KEGG富集分析中均富集到CXCL12a基因,分别富集于免疫反应(GO:0006955)条目和IgA肠道免疫网络(ko04672)通路下。CXCL12[Chemokine(C-X-C motif)ligand 12]即CXC型趋化因子配体12,是一种小分子的细胞因子,与CCL4同属于趋化因子家族,对淋巴细胞有强趋化作用[22]。而CXCL12基因在DESeq分析中,三角鲂相对于团头鲂显著上调,与团头鲂CCL4基因显著上调不同,表明三角鲂和团头鲂抗感染差异可能与招募淋巴细胞、促进细胞吞噬的机制不同相关。方献平等[6]基于蛋白质组学技术发现,相对于团头鲂,三角鲂β-免疫球蛋白感染后显著上调表达。但在本研究中,尽管检测到了β-免疫球蛋白基因表达,但在三角鲂和团头鲂间差异不显著,这可能是由于蛋白应答与基因表达的不同步性[23],或存在其他原因,都有待进一步研究。
参考文献
三角鲂(♀)×翘嘴红鲌(♂)F1及其亲本肌肉成分与必需氨基酸组成模式的比较分析
[J].为比较研究三角鲂、翘嘴红鲌及其杂交F1代的肌肉营养价值的差异,并对杂交种进行营养价值评价,本试验对三种鱼类一般营养成分、氨基酸组成、含量及氨基酸评价等指标进行了比较分析。结果显示,杂交种的粗蛋白含量高于亲本,但粗脂肪含量低于亲本;杂交种的氨基酸总量及必需氨基酸含量都高于亲本;氨基酸指数介于两个亲本之间,且在45%以上;杂交种的氨基酸评分(AAS)大于1.0,化学评分(CS)大于0.5。综合分析结果表明,三角鲂(♀)×翘嘴红鲌 (♂)F1是一种营养价值较高的优质鱼类,其必需氨基酸组成与翘嘴红鲌比较接近。
钱塘江三角鲂线粒体基因组测序及其结构特征分析
[J].为了研究钱塘江流域三角鲂(Megalobrama terminalis Richardson)线粒体基因组结构特征及鲌亚科鱼类的系统进化关系,通过PCR扩增、测序、软件拼接获得了钱塘江三角鲂线粒体基因组全序列,GenBank登录号为MN725725。结果表明,钱塘江三角鲂线粒体基因组序列全长为16 621 bp,碱基组成分别为A(31.23%)、G(16.17%)、C(27.87%)和T(24.73%);共有13个蛋白编码基因,22个tRNA基因,2个rRNA基因,NAD6、tRNA-Gln、tRNA-Ala、tRNA-Asn、tRNA-Cys、tRNA-Tyr、tRNA-Ser<sup>(UCN)</sup>、tRNA-Glu和tRNA-Pro等基因编码在L链上,其余基因均在H链上编码。钱塘江三角鲂线粒体基因组全序列与蛋白编码基因的A+T含量分别为55.97%和55.86%,具有明显的AT偏好性。线粒体基因中存在2个散在重复序列,分别位于线粒体控制区中终止结合序列区的前端和控制区3'的末端。在22个tRNA基因中,除了tRNA-Ser<sup>(AGY)</sup>外,均具有典型的三叶草二级结构。基于BLAST比较,钱塘江三角鲂与黑龙江流域的三角鲂一致性为99.76%,与珠江流域三角鲂一致性为99.87%。基于15种隶属于7属的鲌亚科鱼类线粒体基因组全序列构建的系统进化树,鲂属与鳊属亲缘关系比与鲌属的亲缘关系上较近,与属、半属和细鳊属亲缘关系上较远。
定量蛋白质组学揭示三角鲂和团头鲂响应嗜水气单胞菌侵染机制变化
[J].
Differential expression analysis for sequence count data
[J].
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2
[J].
clusterProfiler:an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters
[J].
RNA-Seq:a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics
[J].
中华鳖性别差异表达基因比较研究
[J].为获得中华鳖(Trionyx sinensis)性别差异表达基因,探索中华鳖性别决定机制,本研究采用RNA-Seq技术测定了中华鳖成熟期精巢和卵巢转录组,分别获得了21 494 396 400 bp和24 605 142 600 bp的clean data。获得总的差异基因10 145个,其中在卵巢中表达上调的有4 034个,在卵巢中表达下调的有6 111个。通过GO、KEGG及蛋白互作分析,在中华鳖性别差异的研究中,获得117个性别表达差异的基因,在雌性中高表达的性别相关基因有Foxl2、Sox3、Sox7、Bmp4、Csf1、Wnk2、Mtmr4、Gsc、Mr2f2、Fgf9、Tgfβ2、Tgfβ3、Rara、Smd2、Smd3和Smad5等;在雄性中高表达性别相关基因有Dmrt1、Amh、Sox30、Cct4、Cct5、Cldn11、Crem、Dhcr24、Dnai2、Dynll1、Gabarap、Herc4、Herpud2、Hexb、Hook1、Hormad1和Smc4等;同时Bmp4通过Smad信号通路调控Foxl2的表达,Foxl2基因为中华鳖雌性生理性别的标志基因。
Identification and characterization of a novel fibronectin in zebrafish
[J].Sequence analysis of zebrafish fibronectin (FN) cDNAs indicates that at least two forms of the protein exist in fish. One form (FN1) is very similar to FNs identified in other vertebrates possessing 12 type I, 2 type II, and 17 type III repeats including two alternative splice sites (EIIIA and EIIIB) and a variable region (V). Zebrafish FN1 contains the RGD cell adhesion site in type III(10) and a second cell-binding site (LDV) in the V region. In addition to this conserved form of FN, a novel truncated form of zebrafish FN (FN2) was identified. The predicted structure of FN2 is identical to FN1 at the N-terminal region possessing 9 type I, 2 type II, and the first 3 type III repeats. Following III(3), FN2 contains a unique 20-amino-acid C-terminal tail that is different from the C-terminus of FN1, lacking the two cysteines that are usually involved in the formation of interchain disulfide bonds. Genomic sequence analysis has revealed that FN2 is generated by an alternative RNA splicing pattern that has not been described for FN in other organisms. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis and RNase protection assays reveal that FN2 mRNA is present in the zebrafish embryo throughout development as well as in cultures of an established liver cell line. Experiments conducted with recombinant FN2 synthesized in insect cells demonstrate that the protein promotes the attachment and spreading of fish embryo cells in culture.Copyright 2001 Academic Press.
Engineering the growth factor microenvironment with fibronectin domains to promote wound and bone tissue healing
[J].
Zebrafish complement factor H and its related genes:identification,evolution,and expression
[J].
Factor H autoantibodies in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome correlate with CFHR1/CFHR3 deficiency
[J].Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is a severe renal disease that is associated with defective complement regulation caused by multiple factors. We previously described the deficiency of factor H-related proteins CFHR1 and CFHR3 as predisposing factor for aHUS. Here we identify in an extended cohort of 147 aHUS patients that 16 juvenile individuals (ie, 11%) who either lacked the CFHR1/CFHR3 completely (n = 14) or showed extremely low CFHR1/CFHR3 plasma levels (n = 2) are positive for factor H (CFH) autoantibodies. The binding epitopes of all 16 analyzed autoantibodies were localized to the C-terminal recognition region of factor H, which represents a hot spot for aHUS mutations. Thus we define a novel subgroup of aHUS, termed DEAP HUS (deficiency of CFHR proteins and CFH autoantibody positive) that is characterized by a combination of genetic and acquired factors. Screening for both factors is obviously relevant for HUS patients as reduction of CFH autoantibody levels represents a therapeutic option.
B cells and professional APCs recruit regulatory T cells via CCL4
[J].Using gene expression profiling, we show here that activation of B cells and professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs) induces the expression of common chemokines. Among these, CCL4 was the most potent chemoattractant of a CD4+CD25+ T cell population, which is a characteristic phenotype of regulatory T cells. Depletion of either regulatory T cells or CCL4 resulted in a deregulated humoral response, which culminated in the production of autoantibodies. This suggested that the recruitment of regulatory T cells to B cells and APCs by CCL4 plays a central role in the normal initiation of T cell and humoral responses, and failure to do this leads to autoimmune activation.
Chemokines enhance immunity by guiding naive CD8+ T cells to sites of CD4+ T cell-dendritic cell interaction
[J].
Regulation of regulators:Role of the complement factor H-related proteins
[J].
The unique structural and functional features of CXCL12
[J].
Quantifying E.coli proteome and transcriptome with single-molecule sensitivity in single cells
[J].Protein and messenger RNA (mRNA) copy numbers vary from cell to cell in isogenic bacterial populations. However, these molecules often exist in low copy numbers and are difficult to detect in single cells. We carried out quantitative system-wide analyses of protein and mRNA expression in individual cells with single-molecule sensitivity using a newly constructed yellow fluorescent protein fusion library for Escherichia coli. We found that almost all protein number distributions can be described by the gamma distribution with two fitting parameters which, at low expression levels, have clear physical interpretations as the transcription rate and protein burst size. At high expression levels, the distributions are dominated by extrinsic noise. We found that a single cell's protein and mRNA copy numbers for any given gene are uncorrelated.