中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis),俗称河蟹、大闸蟹,是中国重要的水产养殖经济物种之一,因生长快速、营养丰富、经济价值高,其养殖规模逐年攀升。但随着企业集约化养殖的发展壮大,养殖密度增加等因素导致中华绒螯蟹发病率上升。此外,环境恶化,细菌、病毒等对中华绒螯蟹养殖的威胁不断增加,如爱德华氏菌、嗜水气单胞菌等致病菌使中华绒螯蟹养殖产业造成巨大的经济损失[1]。因此,丰富中华绒螯蟹免疫防御基础理论知识、寻找安全有效的病害防控方法成为中华绒螯蟹养殖产业中亟待解决的问题。
壳寡糖(Chitosan oligosaccharides,COS),又称低聚壳聚糖,是由2~10个氨基葡萄糖经β-1,4-糖苷键连接而成的低分子量聚糖,可由甲壳素生物酶解而获得。壳寡糖因含有多个活泼的氨基和羟基基团,而具有抗氧化、抗菌、增强免疫、调节肠道、保护肝脏等多种生物学活性,现已在医药及农业等多个领域被广泛研究和应用[2]。作为饲料添加剂或免疫增强剂,壳寡糖不仅能调节动物生理功能,加快新陈代谢,而且具有替代抗生素的潜质,对提高动物生长速度、降低死亡率、改善产品品质等方面均有明显的作用[3-4],因而其在畜、禽、水产养殖中的应用研究不断增多。Zhang B Z[5]将壳寡糖应用到泥鳅(Paramisgurnus dabryanus)的养殖中,发现壳寡糖不仅能改善泥鳅的生长性能、体蛋白含量、肠道消化酶活力和抗氧化能力,还提高了泥鳅对嗜水气单胞菌的抗性。Rahimnejad S等[6]发现壳寡糖能显著提高凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)肝胰脏谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶活性和总抗氧化能力,同时上调其crustin、Pen3和proPo等抗菌肽基因的表达。李振达等[7]在三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)基础饲料中添加一定量的壳寡糖,可以显著提高其血清中酸性磷酸酶、溶菌酶、总超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物酶等活力。袁春营等[8]发现在中华绒螯蟹饲料中适量添加低聚壳聚糖,可以改善其免疫功能,增强机体抵御病原菌的能力。张干等[9]发现饲料中添加低聚壳聚糖,可以提高中华绒螯蟹生长性能、抗氧化能力和非特异性免疫力,减少机体脂肪的沉积。目前,壳寡糖在中华绒螯蟹上的研究多停留在现象描述,如生长性能、抗氧化能力和免疫指标的测定上,而免疫调节分子机制研究并未见报道。因此,本实验通过研究中华绒螯蟹非特异性免疫和抗氧化能力,以及免疫调节机制,旨在为壳寡糖在中华绒螯蟹中的研究和应用提供理论支撑。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料与设计
实验用壳寡糖为本实验室通过生物酶解壳聚糖制备而获得,脱乙酰度≥90%,聚合度分布在2~8,其中壳二糖至壳八糖的占比分别为5.5%、21.1%、31.5%、26.7%、10.9%、2.9%、1.3%。实验用(20±2)g中华绒螯蟹购自江苏省连云港市中华绒螯蟹养殖场,在20~22 ℃淡水中暂养,每天定时更换养殖水体并投喂适当的饵料。暂养7 d后,选择45只附肢完整、个体均匀、健康的中华绒螯蟹,随机分为3组,每组15只,第1组分别注射0.1 mL生理盐水(对照组),第2组分别注射0.1 mL 50 μg·mL-1壳寡糖,第3组分别注射0.1 mL 200 μg·mL-1壳寡糖。
1.2 样品采集
中华绒螯蟹注射壳寡糖24 h后,使用一次性无菌注射器从第三步足基部插入,采集血淋巴并按1∶1与抗凝剂(氯化钠510 mmol·L-1、柠檬酸200 mmol·L-1、葡萄糖100 mmol·L-1、柠檬酸三钠30 mmol·L-1,pH 7.3)混匀,800 g,4 ℃离心10 min,收集血淋巴细胞,液氮速冻,-80 ℃保存备用。
1.3 血清免疫指标检测
取中华绒螯蟹血淋巴离心后的上清液,用于超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)、丙二醛(MDA)、溶菌酶(LZM)、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)、酸性磷酸酶(ACP)、一氧化氮(NO)等活性或含量的检测。以上指标均采用试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所)进行检测。
1.4 RNA提取及实时荧光定量PCR
参考Yu A Q等[10]RNA提取及实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)的方法,利用Trizol试剂(Invitrogen, USA)进行中华绒螯蟹血淋巴细胞总RNA的提取,然后用分光光度计Nanodrop 2000(Thermo Scientific)对提取的RNA进行定量分析,取2 μL RNA用于琼脂糖凝胶电泳,检测RNA的完整性。根据试剂盒PrimeScriptTM 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit(TaKaRa,Japan)的说明书进行cDNA的合成。以获得的cDNA为模板,使用SYBR Premix Ex Taq试剂盒(TaKaRa),按说明书要求设置PCR反应体系和程序,结合表1中基因种类和引物序列,以中华绒螯蟹的β-actin基因作为内参基因,采用ABI-Q6-Flex实时荧光定量PCR仪进行扩增,定量结果采用
1.5 统计分析
从每组中随机选取9只中华绒螯蟹,将3只蟹的血淋巴细胞混合为一个样本,每组3个生物学重复样品(n=3)。实验数据用SPSS 20软件进行统计分析,利用单因素方差分析方法(ANOVA)对不同处理组的差异进行比较,P<0.05表示显著差异,P<0.01表示极显著差异。
2 结果与分析
2.1 壳寡糖对中华绒鳌蟹抗氧化能力和非特异性免疫的影响
与对照组相比,2组壳寡糖处理均极显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血清中SOD和CAT的活性(P<0.01);50 μg·mL-1壳寡糖有提高GSH-PX活性的作用趋势,但差异不显著(P>0.05),200 μg·mL-1壳寡糖极显著提高GSH-PX活性(P<0.01);2组壳寡糖处理均显著降低了中华绒螯蟹血清中MDA含量(P<0.05);50 μg·mL-1壳寡糖有提高LZM活性的作用趋势,但差异不显著(P>0.05),200 μg·mL-1壳寡糖显著提高LZM活性(P<0.05);2组壳寡糖均有提高AKP和ACP活性的作用趋势,但差异不显著(P>0.05);2组壳寡糖均显著增加了中华绒螯蟹血清中一氧化氮的含量(P<0.05)(表2)。
表1 研究中采用的引物序列
Tab.1
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5’-3’) Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| EsToll1-F | CCACTGTCTTGCTCGTCGTCTT | |
| EsToll1-R | CAATGCTCTGGTCAATCTGGTTCTG | |
| EsToll2-F | GCATACCAGGACGACGAACAAG | |
| EsToll2-R | TCAAGGAGGTCACAGTCACAGT | |
| EsMyD88-F | GAACAGGATGCCATTGGTGAAA | |
| EsMyD88-R | GGTGATCTTGAGGTGGATGTAGAGT | |
| EsTube-F | ATTGTGCTGCTGGAGTTGCTGAC | |
| EsTube-R | CATCGTCGGTCGCTTCTTCTTGG | |
| EsPelle-F | TAAGCCAGCAAACAACGGAGCA | |
| EsPelle-R | GAGTCACAGGCAAAGAAGGGGA | |
| EsDorsal-F | CGTCAGCAGCACAGCAGAGAAT | |
| EsDorsal-R | CCCGTATTTCCTCCCTCAACTTCAG | |
| EsSOD-F | CCCAGTTGATGACGTTGAAG | |
| EsSOD-R | CTCGGCTACTGCTCCAAGAA | |
| EsCAT-F | ATCAAGTGTCATTCCTCTTCTCTG | |
| EsCAT-R | CCTTCCCTTCTTTGTTCACCA | |
| EsALF-F | GACGCAGGAGGATGCTAAC | |
| EsALF-R | TGATGGCAGATGAAGGACAC | |
| EsALF3-F | GACGAGGAAGTAGGCTTAGTGGT | |
| EsALF3-R | GGGCTGCTGTTCTCTCTGGA | |
| Esβ-actin-F | GCATCCACGAGACCACTTACA | |
| Esβ-actin-R | CTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCACATC | |
表2 壳寡糖对中华绒鳌蟹抗氧化能力和非特异性免疫的影响
Tab.2
| 项目Items | 壳寡糖/(μg·mL-1) Chitosan oligosaccharides | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50 | 200 | ||||
| 超氧化物歧化酶/(U·mL-1) SOD | 14.90±0.75 | 20.48±1.01** | 21.31±0.61** | |||
| 过氧化氢酶/(U·mL-1) CAT | 4.69±1.71 | 13.62±3.60** | 22.03±4.16** | |||
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶/(U·mL-1) GSH-PX | 134.76±18.36 | 215.40±49.79 | 241.04±23.78** | |||
| 丙二醛/(nmol·mL-1) MDA | 7.33±1.01 | 4.67±0.83* | 4.53±0.61* | |||
| 溶菌酶/(U·mL-1) LZM | 207.46±21.70 | 246.14±39.40 | 293.30±17.06* | |||
| 碱性磷酸酶/(U·mL-1) AKP | 1.34±0.09 | 1.43±0.18 | 1.59±0.51 | |||
| 酸性磷酸酶/(U·mL-1) ACP | 2.08±0.20 | 2.33±0.52 | 2.25±0.47 | |||
| 一氧化氮/(μmol·L-1) NO | 14.00±3.92 | 23.36±2.25* | 34.57±3.53** | |||
注:与对照组相比,*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01),未标注的表示无显著性差异(P>0.05)。以下同此。
Notes: Compared with the control group, values with * meant significant difference (P<0.05), and ** meant extremely significant difference (P<0.01),and unlabeled superscript meant no difference (P>0.05). The same as below.
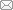
2.2 壳寡糖对Toll样受体表达的影响
图1
图1
壳寡糖对EsToll1 (A) 和EsToll2 (B)基因表达的影响
Fig.1
Effects of chitosan oligosacchrides on expression of EsToll1 (A) and EsToll2 (B)
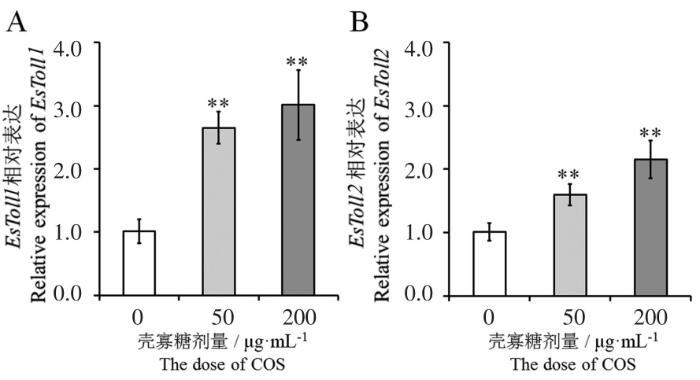
2.3 壳寡糖对Toll信号通路的影响
图2
图2
壳寡糖对EsMyD88 (A)、EsTube (B)、EsPelle (C)和EsDorsal (D)基因表达的影响
Fig.2
Effects of chitosan oligosacchrides on expression of EsMyD88 (A),EsTube (B),EsPelle (C) and EsDorsal (D)
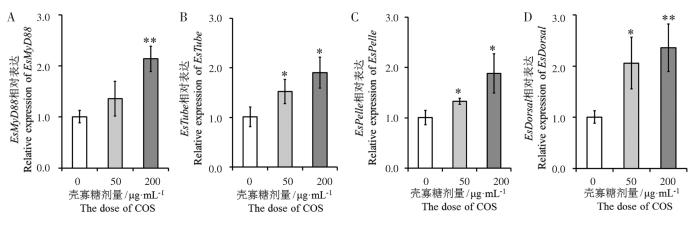
2.4 壳寡糖对免疫效应分子表达的影响
抗氧化酶和抗脂多糖因子作为重要的免疫效应分子,其基因在中华绒螯蟹中分别被命名为EsSOD[15]、EsCAT[16]、EsALF[17]和EsALF3[18]。与对照组相比,50 μg·mL-1壳寡糖处理显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血淋巴细胞EsSOD和EsCAT的表达水平(P<0.05),200 μg·mL-1壳寡糖处理极显著提高了EsSOD和EsCAT的表达水平(P<0.01)(图3A、图3B);50 μg·mL-1壳寡糖处理显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血淋巴细胞EsALF的表达水平(P<0.05),200 μg·mL-1壳寡糖处理极显著提高了EsALF的表达水平(P<0.01)(图3C);2组壳寡糖处理均极显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血淋巴细胞EsALF3的表达水平(P<0.01)(图3D)。
图3
图3
壳寡糖对EsSOD (A)、EsCAT (B)、EsALF (C)和EsALF3 (D)基因表达的影响
Fig.3
Effects of chitosan oligosacchrides on expression of EsSOD (A),EsCAT (B),EsALF (C) and EsALF3 (D)
3 讨论
3.1 壳寡糖对中华绒鳌蟹抗氧化能力的影响
甲壳动物不具有类似脊椎动物的特异性免疫,在复杂的生活环境中,其主要依赖固有免疫系统阻止病原微生物的入侵。甲壳动物免疫系统主要由细胞免疫和体液免疫组成,其中体液免疫主要包括抗氧化酶释放、体液免疫因子、抗菌肽以及凝集素分子等[19]。SOD、CAT和GSH-PX都属于抗氧化体系中重要的生物酶,在机体受到氧化应激时起重要防御作用,反映了甲壳动物的抗应激能力。Niu J等[20]发现壳寡糖可以提高斑节对虾(Penaeus monodon)SOD和GSH-PX的活力,进而提升其总抗氧化能力,减少机体中MDA的含量;在中华绒螯蟹中,张干等[9]同样发现壳寡糖提高了蟹肌肉和可食内脏中SOD和CAT的活性;在本研究中,壳寡糖显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血清中SOD、CAT和GSH-PX的活力,降低了MDA的含量,与Niu J等、张干等的研究结果基本一致。溶菌酶、碱性磷酸酶和酸性磷酸酶都属于体液免疫因子,在甲壳动物体液免疫过程中起非常重要的作用,反映了机体的免疫防御能力。李振达等[7]在三疣梭子蟹中证明壳寡糖可以显著提高血清中LZM 和ACP的活力,但对AKP 活力促进效果不显著;袁春营等[8]在中华绒螯蟹中同样发现壳寡糖可以提高血清中LZM的活力;而在本研究中,壳寡糖显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血清中LZM活力,对AKP和ACP活力有提高的作用趋势,但差异不显著,这与李振达等、袁春营等的研究结果有所不同,可能与壳寡糖作用的时间有一定的关系。一氧化氮作为细胞内重要的信号分子,在脊椎动物和无脊椎动物免疫反应中均发挥着重要作用。Jiang Q F等[21]对栉孔扇贝(Chlamys farreri)的研究发现,一氧化氮参与了栉孔扇贝免疫,对其血淋巴的免疫应答、血细胞凋亡与吞噬、抗菌活性和氧化还原平衡起着重要的调节作用。Raman T等[22]在罗氏沼虾(Macrobrachium rosenbergii)中同样发现,一氧化氮参与了凝集素介导的虾血细胞吞噬反应,若使用一氧化氮抑制剂,则可有效抑制上述吞噬反应。在本研究中,壳寡糖显著提高了中华绒螯蟹血清中一氧化氮的水平,提示其可能参与了中华绒螯蟹的免疫反应过程。
3.2 壳寡糖的免疫调节机制
Toll信号通路能够激活多种免疫相关基因(如小分子蛋白、抗菌肽以及吞噬作用和黑化作用相关基因等)来响应细菌和病毒的入侵。在甲壳类动物中,Toll通路主要包括Toll样受体、MyD88、Tube、Pelle和Dorsal等关键分子[23]。Yu A Q等[11]在中华绒螯蟹中成功克隆表达了EsToll1和EsToll2分子,并且证明两者均参与了中华绒螯蟹对脂多糖、酵母聚糖和肽聚糖的免疫响应。本研究也发现壳寡糖可以有效诱导中华绒螯蟹血淋巴细胞Toll样受体的表达。此外,研究学者在中华绒螯蟹中已经成功地证明存在着Toll信号通路,并鉴定了EsMyD88[12]、EsTube[13]、EsPelle[14]和EsDorsal[10]等关键分子,这些分子在不同的免疫刺激物作用下呈现出不同的免疫响应过程。本研究发现壳寡糖可以有效地上调EsMyD88、EsTube、EsPelle和EsDorsal的表达,提示壳寡糖可能通过开启Toll信号通路发挥其免疫调节作用。抗氧化酶体系是甲壳动物重要的免疫防御手段,壳寡糖上调了中华绒螯蟹血淋巴细胞EsSOD和EsCAT的表达,这与中华绒螯蟹血清抗氧化酶活力变化趋势基本一致。抗菌肽是体液免疫的重要效应分子,能有效杀灭细菌等,是机体免疫的有效屏障,同时抗菌肽的表达受到Toll信号通路的调控。在中华绒螯蟹中,研究学者先后鉴定出抗脂多糖因子EsALF和EsALF3等多种抗菌肽,这些抗菌肽在甲壳动物的免疫防御过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用[17-18]。本研究发现壳寡糖可以显著提高EsALF和EsALF3的表达水平,提示壳寡糖的免疫调节机制可能是通过Toll信号通路介导的抗菌肽来发挥作用。
4 结论
壳寡糖可以改善中华绒螯蟹的抗氧化能力和非特异性免疫功能,增强Toll信号通路中EsToll1、EsToll2、EsMyD88、EsTube、EsPelle和EsDorsal的表达,上调抗脂多糖因子EsALF和EsALF3的表达。
参考文献
江苏河蟹产业科技创新发展现状与趋势研究
[J].专利信息是掌握特定技术领域技术布局与发展趋势的重要途径之一。通过人工标引方法对江苏河蟹产业相关的有权专利和审中专利进行分析,基本掌握了现阶段江苏河蟹产业专利技术布局与未来发展趋势。专利技术布局特点为:无锡、南京、常州、宿迁和苏州5个地区是江苏河蟹产业有权专利技术的主要区域创新中心,科研院所是江苏河蟹产业专利权人的主要类型,扣蟹养殖过程在有权专利中受关注度最高。科技创新的发展趋势为:南京、无锡、苏州、镇江、泰州、常州、盐城和淮安8个地区是江苏河蟹产业科技创新的潜在区域创新中心,企业成为审中专利的主要创新主体,创新领域更加注重全产业链。提出推动射阳港现代水产种业产业园建设、加强配合饲料替代幼杂鱼投喂技术研发应用、大力推广河蟹养殖绿色发展模式等对策建议,以促进江苏河蟹产业绿色高质量发展。
Chitooligosaccharides and their biological activities:a comprehensive review
[J].
A review on the preparation of chitosan oligosaccharides and application to human health, animal husbandry and agricultural production
[J].Chitosan oligosaccharides (COS) are the degraded products of chitin or chitosan prepared by chemical or enzymatic hydrolysis. As compared to chitosan, COS not only exhibit some specific physicochemical properties such as excellent water solubility, biodegradability and biocompatibility, but also have a variety of functionally biological activities including anti-inflammation, anti-bacteria, immunomodulation, neuroprotection and so on. This review aims to summarize the preparation and structural characterization methods of COS, and will discuss the application of COS or their derivatives to human health, animal husbandry and agricultural production. COS have been demonstrated to prevent the occurrence of human health-related diseases, enhance the resistance to diseases of livestock and poultry, and improve the growth and quality of crops in plant cultivation. Overall, COS have presented a broad developmental potential and application prospect in the healthy field that deserves further exploration.Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
几丁质脱乙酰酶的特点及应用
[J].几丁质是渔业生产过程中废弃虾蟹壳的主要组成成分。传统生产几丁质、壳聚糖和壳寡糖的方法是化学消化法,此方法的主要问题是环境污染严重,随着人们环保意识的提高,该方法已难以持续。此外由于化学法生产的壳聚糖和壳寡糖难以控制其聚合度、脱乙酰度和脱乙酰模式,因此很难研究壳寡糖的结构与功能之间的关系。几丁质脱乙酰酶(Chitin deacetylase EC 3.5.1.4 1 )是一种可在温和条件下将几丁寡糖转化为壳寡糖的酶,利用此酶规模化生产具有特定乙酰化模式的壳寡糖已成为一个很重要的研究方向。鉴于该酶对于产业发展的重要性,本文对目前已经研究的几丁质脱乙酰酶的来源、结构特征、催化机制、脱乙酰化模式及几丁质脱乙酰化酶的应用等方面进行了综述。
Dietary chitosan oligosaccharides modulate the growth, intestine digestive enzymes, body composition and nonspecific immunity of loach Paramisgurnus dabryanus
[J].
Chitooligosaccharide supplementation in low-fish meal diets for Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): effects on growth, innate immunity, gut histology, and immune-related genes expression
[J].
Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a dorsal homologue from Eriocheir sinensis
[J].
Two novel Toll genes (EsToll1 and EsToll2) from Eriocheir sinensis are differentially induced by lipopolysaccharide, peptidoglycan and zymosan
[J].
Novel myeloid differentiation factor 88, EsMyD88, exhibits EsTube-binding activity in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
[J].Myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) is a universal and essential adapter protein that participates in the activation of the Toll-like receptor/interleukin-1 receptor-mediated signaling pathway. In the present study, a new MyD88 gene (named EsMyD88) was identified in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. The cDNA of EsMyD88 was 2210 bp long with a 1416 bp open reading frame that encoded a protein with 472 amino acids. Predicted EsMyD88 protein had a death domain at the N-terminal and a TIR domain at the C-terminal. BLASTP and phylogenetic analysis results showed that EsMyD88 was clustered in one group together with other crustaceans MyD88 (SpMyD88, FcMyD88, LvMyD88, and LvMyD88-1). EsMyD88 was detected in all the examined tissues of healthy crabs, and was mainly expressed in the hemocytes and nerves. When normal crabs were challenged with lipopolysaccharide, peptidoglycan, Staphylococcus aureus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, or Aeromonas hydrophila, the expression levels of EsMyD88 significantly increased either in the hepatopancreas or hemocytes. Results of the pull-down assay showed that EsMyD88 could bind to downstream cytosolic adaptor EsTube. Overexpression of EsMyD88 protein in Drosophila Schneider 2 cells led to the activation of antimicrobial peptide genes. RNA interference assay showed that EsMyD88 is involved in regulating the transcription of ALF1 and ALF2, Cru1 and Cru2, and Lys in crab challenged with V. parahaemolyticus. All the results mentioned earlier indicated that EsMyD88 gene has a key function in antibacterial innate immune defense.Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Identification and characterization of Tube in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
[J].
Identification, characterization, and functional studies of a Pelle gene in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis
[J].
Molecular cloning and characterization of a cytoplasmic manganese superoxide dismutase and a mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase from Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
[J].
The molecular characterization of a catalase from Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
[J].Catalase (CAT) is an antioxidant enzyme and plays a significant role in the protection against oxidative stress by reducing hydrogen peroxide. The CAT cDNA of Eriocheir sinensis (EsCAT) was cloned via RACE technique. The complete sequence of EsCAT cDNA consisted of a 5' untranslated regions (UTR) of 224 bp, a 3' UTR of 1287 bp with a poly (A) tail and an open reading frame (ORF) of 1542 bp, which encoded a polypeptide of 513 amino acid residues with a calculated molecular mass of approximately 58.86 kDa and a theoretical isoelectric point of 6.880. The deduced amino acid sequence of EsCAT contained a highly conserved proximal active-site signature motif ((60)FDRERIPERVVHAKGAL(76)) and a proximal heme-ligand signature motif ((350)RLFSYNDTH(358)) and exhibited high similarity with other reported CATs. In the phylogenetic tree, EsCAT was clustered with the CATs from Scylla serrata and Portunus trituberculatus. The EsCAT transcripts were constitutively expressed in haepatopancreas, haemocytes, gill, gonad, muscle and heart, with highest expression level in haepatopancreas. The relative expression level of EsCAT mRNA in haemocytes was continuously up-regulated and reached the peak level at 48 h post-Vibrio anguillarum challenge. The purified recombinant EsCAT protein displayed antioxidant activity against hydrogen peroxide with high thermal stability and broad spectrum of pH values. All these results demonstrated that EsCAT was an efficient antioxidant enzyme and potentially involved in the regulation of redox and innate immune response of crabs.© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Molecular cloning, genomic organization and functional analysis of an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis
[J].
A new anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (EsALF-3) from Eriocheir sinensis with antimicrobial activity
[J].
Invertebrate immune systems specific, quasi-specific, or nonspecific?
[J].Until recently, it was widely accepted that invertebrates fail to show a high degree of specificity and memory in their immune strategies. Recent reports have challenged this view such that our understanding of the capabilities of the invertebrate immune systems needs to be reassessed. This account critically reviews the available evidence that suggests the existence of a high degree of memory and specificity in some invertebrates and seeks mechanistic explanations of such observations. It is postulated that elevated levels of phagocytosis may be a partial explanation for this phenomenon.
Comparison of effect of chitin, chitosan, chitosan oligosaccharide and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine on growth performance, antioxidant defenses and oxidative stress status of Penaeus monodon
[J].
The immunomodulation of inducible nitric oxide in scallop Chlamys farreri
[J].
Agglutinin-mediated phagocytosis-associated generation of superoxide anion and nitric oxide by the hemocytes of the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii
[J].
Signaling pathways regulating innate immune responses in shrimp
[J].